Salicylic acid for acne is a popular topical treatment, known for its ability to gently exfoliate and unclog pores. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of using salicylic acid to manage acne, from its chemical properties and mechanisms of action to potential side effects and comparisons with other treatments.
Understanding the different concentrations, application methods, and suitability for various skin types and acne severities is crucial for achieving optimal results. This guide aims to provide a detailed and accessible overview for anyone considering salicylic acid as part of their acne management strategy.
Introduction to Salicylic Acid for Acne
Salicylic acid is a common ingredient in topical acne treatments. Its effectiveness stems from its unique chemical properties, allowing it to penetrate pores and exfoliate the skin, addressing the root causes of acne. This detailed look at salicylic acid will explore its role in acne treatment, its chemical makeup, and the various forms it comes in.Salicylic acid’s chemical structure makes it a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA).
Crucially, its lipophilic (fat-loving) and hydrophilic (water-loving) properties enable it to dissolve in both oil and water. This dual solubility is key to its ability to penetrate pores clogged with sebum and dead skin cells, a primary driver of acne. This penetration facilitates the exfoliation process, helping to unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
Salicylic acid is a popular ingredient for treating acne. It works by exfoliating the skin and unclogging pores. Finding the right salicylic acid product can be tricky, but checking out some of the best skincare products available can help you find one that works well for your skin type. Ultimately, a good salicylic acid product is key for managing acne breakouts effectively.
Forms of Salicylic Acid
Various topical formulations of salicylic acid exist to cater to different needs and preferences. These include lotions, gels, and pads, each with a distinct consistency and potential application method. Lotions are typically more hydrating, while gels are thinner and quicker-absorbing. Pads often provide a convenient and precise application method.
Salicylic Acid Concentrations and Potential Uses
The concentration of salicylic acid in a topical product significantly impacts its efficacy and potential side effects. A table below Artikels common concentrations and their typical use cases. Important note: always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
| Concentration | Typical Use | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-2% | Mild acne, preventative skincare | Mild skin irritation, redness, dryness |
| 2-5% | Moderate acne, treatment of existing breakouts | Increased risk of skin irritation, peeling, burning sensation |
| 7-10% | Severe acne, treatment of comedones and papules | Significant skin irritation, peeling, potential for increased sensitivity |
Mechanisms of Action: Salicylic Acid For Acne
Salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA), plays a crucial role in acne treatment by targeting multiple aspects of the condition. Its unique properties allow it to effectively address clogged pores, excess sebum production, and inflammation, all key contributors to acne development.Salicylic acid’s effectiveness stems from its ability to penetrate the skin and exert its therapeutic effects within the skin’s layers.
This enables it to address the root causes of acne, promoting clearer and healthier skin.
Exfoliation
Salicylic acid’s exfoliating properties are a key mechanism in its acne-fighting action. It dissolves the bonds between corneocytes, the dead skin cells that can accumulate on the skin’s surface and clog pores. This process, known as keratolysis, effectively removes these accumulated cells, preventing pore blockages and promoting smoother skin texture. The removal of dead skin cells also allows for better penetration of other acne treatments.
Unclogging Pores
Salicylic acid’s ability to dissolve the bonds between corneocytes, mentioned previously, directly contributes to unclogging pores. This action is facilitated by its lipophilic nature, which allows it to penetrate into the pores and effectively remove the accumulated sebum and dead skin cells that cause blockage. This, in turn, prevents the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) and reduces the risk of infection.
Impact on Sebum Production
While salicylic acid itself does not directly regulate sebum production, its overall effect on skin health can indirectly influence sebum levels. By reducing inflammation and promoting cell turnover, salicylic acid can create a more balanced skin environment, potentially leading to a decrease in excess sebum production. However, further research is needed to fully understand the precise mechanisms involved.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of salicylic acid in treating acne. These studies have shown a reduction in the number of lesions, including comedones and inflammatory papules, in individuals using salicylic acid-based products. For example, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology reviewed several studies and concluded that topical salicylic acid is effective in treating acne vulgaris.
Reducing Inflammation
Salicylic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the redness and swelling associated with acne. By reducing the inflammatory response, salicylic acid can prevent the formation of pustules and nodules, thus promoting faster healing and a less inflamed complexion. Furthermore, it may inhibit the activity of inflammatory mediators, which play a critical role in the development of acne.
Types of Acne and Salicylic Acid Treatment
Salicylic acid is a popular and effective treatment for various acne types. Its keratolytic properties, meaning it helps exfoliate the skin, make it a valuable tool in managing different forms of acne. Understanding how salicylic acid interacts with various acne types and triggers is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes.Salicylic acid’s effectiveness in treating acne is often linked to its ability to target the underlying causes of breakouts.
By addressing the root causes, salicylic acid can significantly improve acne severity and appearance.
Suitability for Different Acne Types
Salicylic acid is particularly well-suited for comedonal acne, which is characterized by clogged pores and blackheads. Its keratolytic action helps unclog pores, preventing further buildup and reducing the formation of comedones. However, salicylic acid can also be beneficial for inflammatory acne, although its primary focus is on reducing the blockage that leads to inflammation. For severe inflammatory acne, additional treatments might be necessary alongside salicylic acid.
Effectiveness Against Acne Triggers
Salicylic acid demonstrates efficacy against various acne triggers. Its keratolytic properties help control excess sebum production, a significant contributor to acne development. Furthermore, salicylic acid can help control the growth of
- Cutibacterium acnes* (formerly known as
- Propionibacterium acnes*), a bacterium commonly associated with acne. This dual action of controlling sebum and bacterial overgrowth makes salicylic acid a comprehensive treatment option.
Salicylic Acid Concentration by Acne Severity
| Acne Severity | Recommended Salicylic Acid Concentration | Additional Treatment Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Comedonal Acne | 0.5-2% | Consider topical retinoids or benzoyl peroxide for added benefits. |
| Moderate Comedonal Acne | 2-5% | May require combination therapy with topical retinoids or benzoyl peroxide. A visit to a dermatologist might be necessary. |
| Mild Inflammatory Acne | 2-5% | Consider incorporating topical antibiotics, if appropriate, to address bacterial overgrowth. |
| Moderate Inflammatory Acne | 5-10% | A consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to develop a personalized treatment plan, which might include oral medications in addition to topical salicylic acid. |
| Severe Inflammatory Acne | 10% (or higher, as determined by a dermatologist) | A consultation with a dermatologist is essential to develop an effective treatment plan, potentially including oral antibiotics, isotretinoin, or other targeted therapies. |
Note: Concentrations and suitability are specific to individual needs and should be determined by a healthcare professional. It is crucial to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when using salicylic acid.
Application Methods and Procedures
Proper application of salicylic acid is crucial for its effectiveness and to minimize potential skin irritation. Adhering to the recommended application methods and procedures is vital for achieving the desired results while preventing adverse reactions. Consistent and correct application is key to managing acne effectively.
Proper Application Methods
Salicylic acid products should be applied gently and evenly to affected areas. Avoid scrubbing or harsh rubbing, as this can further irritate the skin. Use a clean fingertip or a cotton swab to apply the product. Ensure the product is distributed evenly across the affected area.
Step-by-Step Guide for Topical Application
- Cleanse the affected area thoroughly with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup. This prepares the skin for optimal product absorption.
- Apply a small amount of salicylic acid to the affected area using a fingertip or cotton swab. Avoid applying too much product, as this can lead to over-application and irritation.
- Gently spread the salicylic acid in a thin, even layer over the targeted area. Do not rub or scrub vigorously. Apply evenly, covering the affected area completely.
- Allow the product to dry completely before applying any other skincare products. This allows the salicylic acid to work effectively.
- Follow up with a moisturizer, if needed, after the product has fully dried. This can help soothe any potential irritation.
Avoiding Over-Application
Over-application of salicylic acid can lead to skin irritation, redness, and dryness. It’s important to follow the product instructions carefully and use the recommended amount for each application. Starting with a lower concentration of salicylic acid and gradually increasing as tolerated is a recommended approach. Using a smaller amount than suggested is preferable to using excessive amounts.
Optimal Frequency of Application
The optimal frequency of application depends on individual skin sensitivity and the product’s concentration. Generally, starting with once daily application is a good starting point. If using a higher concentration, or experiencing significant irritation, it may be necessary to reduce the frequency to every other day or even less. Observe how your skin reacts to the product and adjust the frequency accordingly.
Always listen to your skin’s signals.
Potential Interactions with Other Skincare Products
Salicylic acid can interact with other skincare products, potentially affecting its efficacy or causing irritation. For instance, combining salicylic acid with products containing strong exfoliants or alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) might lead to increased skin sensitivity. Be mindful of the ingredients in your other skincare products and adjust the application schedule accordingly, or consider consulting a dermatologist.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Salicylic acid, while effective for acne treatment, can sometimes cause skin irritation. Understanding potential side effects and taking necessary precautions is crucial for safe and effective use. Proper application techniques and attentive monitoring are essential to minimize any negative reactions.Salicylic acid’s exfoliating properties can lead to mild to moderate skin reactions, ranging from redness and dryness to more severe irritation.
Careful attention to these potential side effects is paramount for a positive treatment outcome. This section details common side effects, management strategies, and important precautions to ensure a safe and effective acne treatment regimen.
Common Side Effects
Mild side effects are often manageable and temporary. These can include redness, dryness, and mild stinging or burning sensations. These reactions typically subside as the skin adapts to the product. Severe or persistent reactions warrant immediate discontinuation and consultation with a dermatologist.
- Redness: A common reaction, often associated with inflammation or irritation. This typically subsides within a few hours to a few days, depending on the individual’s skin sensitivity and the concentration of salicylic acid used.
- Dryness: Salicylic acid can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and flakiness. Applying a moisturizer can help alleviate this issue.
- Stinging/Burning: These sensations often indicate the product is too strong for the individual’s skin. A lower concentration of salicylic acid or a different application method may be necessary.
- Exfoliation: Salicylic acid promotes exfoliation. While this is beneficial for acne treatment, excessive exfoliation can lead to visible flakiness and potentially worsen skin sensitivity.
Managing Skin Irritation
Skin irritation from salicylic acid is a common occurrence, particularly in those with sensitive skin or when using high concentrations. Appropriate management strategies can alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
- Reduce Frequency: Gradually introduce salicylic acid into your routine. Start with a lower frequency (e.g., every other day) and gradually increase as tolerated. This approach allows the skin to adapt.
- Dilute the Product: If the product is too strong, dilute it with a non-irritating moisturizer. This can help to lessen the impact of the active ingredient on the skin.
- Use a Gentle Cleanser: A mild, fragrance-free cleanser can help prevent further irritation or dryness. Avoid harsh scrubbing or abrasive cleansers.
- Moisturize Regularly: Maintaining skin hydration is crucial. A non-comedogenic moisturizer, specifically designed for sensitive skin, can effectively replenish lost moisture and reduce dryness.
Patch Testing
A patch test is essential to assess individual skin reactions before widespread use. This method identifies potential sensitivities and ensures the product is suitable for the individual’s skin.
- Procedure: Apply a small amount of salicylic acid to a small, inconspicuous area of skin, such as the inside of the forearm or behind the ear. Monitor the area for any signs of irritation for 24-48 hours.
- Interpretation: If no irritation develops, the salicylic acid is likely suitable for widespread use. However, if any reaction arises (e.g., redness, itching, blistering), discontinue use immediately and consult a dermatologist.
Discontinuing Use
If irritation persists despite management strategies, discontinue use immediately. Consulting a dermatologist can help determine the appropriate course of action and alternative treatment options.
- Gradual Reduction: If the irritation is mild, consider gradually reducing the frequency or concentration of the product until the irritation subsides.
- Consultation: If the irritation is severe or does not improve, immediately consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and alternative treatment options.
Allergic Reactions
While less common than skin irritation, allergic reactions to salicylic acid are possible. Prompt identification and management are crucial.
- Symptoms: Allergic reactions may manifest as hives, swelling, itching, or difficulty breathing. These reactions can vary in severity.
- Action: If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue use immediately and seek immediate medical attention.
Salicylic Acid vs. Other Acne Treatments
Salicylic acid is a popular over-the-counter acne treatment, often preferred for its ability to exfoliate the skin and unclog pores. However, it’s important to understand how its effectiveness compares to other common treatments like benzoyl peroxide and retinoids. This comparison considers their mechanisms of action, potential benefits, and drawbacks, helping users make informed decisions about their acne care.Comparing salicylic acid with other acne treatments reveals nuances in their approaches to skin health.
Each treatment targets different aspects of acne formation, leading to varying degrees of effectiveness and potential side effects. Understanding these distinctions can help individuals tailor their acne management strategies for optimal results.
Effectiveness Comparisons
Salicylic acid’s effectiveness in treating acne is often attributed to its keratolytic properties. It works by dissolving the bonds that hold dead skin cells together, promoting exfoliation and unclogging pores. Benzoyl peroxide, on the other hand, acts as an antibacterial agent, targeting the bacteria that contribute to acne formation. Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, influence cell turnover and oil production, thereby preventing the formation of acne lesions.
The effectiveness of each treatment can vary significantly depending on the individual’s skin type, acne severity, and the specific product formulation.
Situations Favoring Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is often a suitable choice for individuals with mild to moderate acne, particularly those experiencing comedonal acne (blackheads and whiteheads). Its keratolytic action is particularly effective in dissolving these types of blemishes. In cases where irritation or dryness is a concern, salicylic acid may be a gentler option than retinoids, especially in its lower concentrations. However, for severe acne or cystic acne, other treatments might be more suitable.
Salicylic acid is a common ingredient for treating acne, known for its exfoliating properties. Many Korean skincare routines incorporate this ingredient, often in various forms like serums or toners, as part of a multi-step approach to clear skin. The focus on exfoliation and ingredient synergy in a Korean skincare routine can be highly effective in targeting acne.
This makes salicylic acid a valuable tool in managing acne, particularly when used consistently within a well-rounded skincare regimen.
Combining Treatments
Combining salicylic acid with other acne treatments can offer synergistic benefits. For instance, using salicylic acid in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide can provide a multifaceted approach to acne management. Salicylic acid can improve the penetration of benzoyl peroxide, leading to enhanced antibacterial effects. Combining salicylic acid with retinoids can also be beneficial, though this combination may increase the risk of skin irritation.
It’s crucial to consult a dermatologist to determine the optimal combination strategy and to monitor for any potential adverse reactions.
Table Comparing Acne Treatments
| Treatment | Ingredients | Benefits | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salicylic Acid | Salicylic acid | Effective for comedonal acne, keratolytic action, often gentler than other treatments | Skin irritation, dryness, redness, peeling, allergic reactions (less common) |
| Benzoyl Peroxide | Benzoyl peroxide | Effective antibacterial agent, combats acne-causing bacteria | Skin irritation, dryness, redness, itching, potential for skin discoloration |
| Retinoids | Retinoids (e.g., retinol, tretinoin) | Influences cell turnover, reduces oil production, effective for various acne types | Skin irritation, dryness, redness, peeling, sensitivity to sunlight |
Salicylic Acid for Specific Skin Types
Salicylic acid, a popular acne treatment, can be effectively tailored for various skin types. Understanding how to adjust application methods and concentrations is crucial for maximizing its benefits and minimizing potential side effects. This section will delve into adapting salicylic acid for different skin types, including oily, dry, and sensitive skin, and will also touch upon combining it with other skincare routines and pre-existing skin conditions.Different skin types react differently to salicylic acid.
Oily skin often benefits from its exfoliating properties, while dry skin might require a more gentle approach. Understanding these nuances allows for a personalized skincare routine that caters to individual needs and prevents irritation.
Adapting Salicylic Acid for Different Skin Types
Salicylic acid’s effectiveness is enhanced by tailoring its application based on skin type. Oily skin, often prone to acne breakouts, can tolerate higher concentrations of salicylic acid. Conversely, individuals with dry or sensitive skin should start with a lower concentration and gradually increase it as tolerated.
Application Methods for Various Skin Types
The application method plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results while minimizing potential irritation.
- Oily Skin: A higher concentration of salicylic acid (e.g., 2%) can be used once or twice daily. It is important to avoid over-drying the skin. A hydrating moisturizer should be applied after using salicylic acid.
- Dry Skin: A lower concentration of salicylic acid (e.g., 0.5%) should be used once daily, ideally in the evening. It’s essential to follow up with a rich, hydrating moisturizer to prevent dryness and flakiness.
- Sensitive Skin: A very low concentration of salicylic acid (e.g., 0.2%) should be used once daily, preferably at night. Using a gentle cleanser and a soothing moisturizer is crucial to prevent redness and irritation.
Combining Salicylic Acid with Other Skincare Routines
Salicylic acid can be integrated into a comprehensive skincare routine effectively.
- Exfoliating Scrubs: Combining salicylic acid with exfoliating scrubs can be beneficial for oily skin. However, avoid frequent use of exfoliating scrubs to prevent skin irritation, especially for dry or sensitive skin.
- Moisturizers: Moisturizers are crucial to balance the exfoliating effect of salicylic acid, particularly for dry or sensitive skin types. Choose a moisturizer that is non-comedogenic and suitable for your skin type.
- Sunscreen: Applying sunscreen after using salicylic acid is important, as the treatment can make skin more sensitive to UV rays.
Adjusting Concentration and Frequency of Application
The concentration and frequency of salicylic acid application should be adjusted based on individual skin type and response. Start with a lower concentration and frequency, and gradually increase as tolerated.
- Gradual Increase: Begin with a lower concentration (e.g., 0.5% for dry skin) and use it once daily. If there’s no adverse reaction, gradually increase the concentration and/or frequency as needed.
- Monitoring Skin Response: Closely monitor your skin’s response to salicylic acid. If irritation or dryness occurs, reduce the concentration or frequency of application.
- Consistency: Consistency is key to seeing results. Even with adjusted concentrations, consistent use is essential for optimal outcomes.
Considerations for Pre-existing Skin Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions (e.g., eczema, rosacea) should use salicylic acid cautiously. Consult a dermatologist before incorporating salicylic acid into your skincare routine.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you have pre-existing skin conditions, consult a dermatologist before using salicylic acid. They can assess your specific skin needs and recommend appropriate concentrations and application methods.
- Start with Low Concentrations: Begin with the lowest possible concentration and gradually increase it as tolerated, always monitoring for any adverse reactions.
- Individualized Approach: A dermatologist can tailor a salicylic acid treatment plan based on your specific skin condition and needs.
Long-Term Use and Maintenance
Salicylic acid can be a valuable tool in managing acne, but its long-term use requires careful consideration. Understanding the potential benefits and risks, as well as implementing proper maintenance strategies, is crucial for achieving and sustaining healthy skin. This section explores the long-term implications of salicylic acid treatment and provides guidance on its safe and effective integration into a daily routine.Maintaining consistent skin health while using salicylic acid involves more than just applying the product.
A comprehensive approach encompassing skincare routines, lifestyle factors, and potential adjustments to the treatment plan is essential for achieving lasting results.
Long-Term Benefits of Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid, when used appropriately and consistently, can contribute to long-term improvements in acne. It effectively exfoliates the skin, reducing the buildup of dead skin cells that can clog pores and lead to breakouts. This, in turn, can help prevent future acne formation and promote clearer, smoother skin over time. Regular use can also help to regulate sebum production, a key factor in acne development.
Some individuals experience reduced inflammation and redness associated with acne, leading to a more even skin tone in the long run.
Long-Term Risks and Considerations
While salicylic acid is generally safe, prolonged or excessive use can lead to potential side effects. Over-exfoliation can lead to skin dryness, irritation, and sensitivity. Frequent use of high concentrations can also thin the skin’s protective barrier, increasing its vulnerability to environmental factors. If you experience persistent dryness, redness, or irritation, it’s crucial to adjust your routine or consult a dermatologist.
Maintaining Skin Health, Salicylic acid for acne
Maintaining skin health during salicylic acid use is essential. A balanced skincare routine is key. A gentle cleanser, followed by a moisturizer, is crucial, particularly if you experience dryness or irritation. Avoid harsh scrubbing or over-exfoliating, and ensure adequate hydration. Dietary choices also play a significant role.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and water can contribute to overall skin health.
Preventing Acne Recurrence
Preventing acne recurrence after treatment requires a proactive approach. Consistency in using salicylic acid, as prescribed, is vital for optimal results. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, including regular cleansing, moisturizing, and appropriate sun protection, is crucial. Addressing underlying factors like stress and sleep patterns can also contribute to preventing future breakouts. In some cases, combining salicylic acid with other treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide or retinoids, might be necessary for more severe acne.
A Simple Salicylic Acid Routine
This routine provides a framework for incorporating salicylic acid into a daily skincare regimen.
- Morning: Cleanse the face with a gentle cleanser. Apply a pea-sized amount of salicylic acid serum or lotion, avoiding the eye area. Follow with a moisturizer that suits your skin type. Apply sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Evening: Cleanse the face again. Repeat the salicylic acid application. Apply a gentle, hydrating night cream. Ensure you are consistent with these steps, as this contributes significantly to long-term skin health.
Product Selection and Reviews
Choosing the right salicylic acid product for your acne treatment can significantly impact your results. Understanding the various formulations and carefully evaluating product reviews are crucial for effective and safe use. This section provides guidance on selecting suitable products and evaluating online reviews.
Recommended Salicylic Acid Products
Several salicylic acid products are available, each with varying concentrations and formulations. A dermatologist or skincare professional can provide personalized recommendations based on your skin type and acne severity. General recommendations include products with a concentration of 0.5-2% salicylic acid, depending on your skin sensitivity. Popular brands often feature a range of concentrations and formulations, catering to different needs.
Selecting Products for Individual Needs
Selecting the right salicylic acid product depends on factors such as skin type, acne severity, and sensitivity. Products with lower concentrations (e.g., 0.5-1%) are generally better suited for sensitive skin or those new to salicylic acid. For moderate acne, a 1-2% concentration might be appropriate. It’s vital to consider the additional ingredients in the product, as some may exacerbate skin sensitivities.
Reading Product Labels Carefully
Thorough examination of product labels is paramount for effective and safe use. Look for the percentage of salicylic acid, the presence of potential irritants or allergens, and any specific instructions for application. Pay close attention to the list of ingredients, as other components can influence your skin’s response.
Evaluating Online Reviews
Online reviews can offer valuable insights, but it’s essential to approach them critically. Look for reviews from individuals with similar skin types and acne concerns. Be wary of overly positive or negative reviews that might not represent the product’s overall effectiveness or safety profile. Focus on reviews that describe specific experiences, including product application, perceived results, and any side effects.
Key Features and Benefits to Consider
When selecting a salicylic acid product, consider the following key features and benefits:
- Concentration: Choose a concentration suitable for your skin type and acne severity. Lower concentrations are often better for sensitive skin.
- Formulation: Different formulations (e.g., gel, lotion, cream) may offer varying levels of penetration and application ease.
- Additional Ingredients: Consider the presence of additional ingredients, as some may be irritating or exacerbate skin conditions. Products with soothing or hydrating components can be beneficial for sensitive skin.
- Reviews: Evaluate online reviews from individuals with similar skin types and acne concerns, focusing on consistency and specific experiences.
- Price and Availability: Consider the product’s cost and ease of accessibility. Compare prices and availability from different retailers.
Expert Advice and Recommendations
Seeking professional guidance is crucial when incorporating salicylic acid into your skincare routine. A dermatologist or skincare specialist can tailor recommendations to your specific skin type, concerns, and existing conditions. This personalized approach ensures optimal results and minimizes potential risks.Dermatologists and skincare specialists possess extensive knowledge of various skin conditions and the appropriate use of active ingredients like salicylic acid.
They can accurately assess your skin’s health, identify any underlying issues, and prescribe the most suitable salicylic acid product and concentration for your needs.
Importance of Professional Consultation
A consultation with a qualified healthcare provider is essential for safe and effective salicylic acid use. They can evaluate your skin’s sensitivity, current acne severity, and potential interactions with other medications or products. This personalized assessment allows for a precise treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and promotes skin health. Avoid self-treating or relying solely on online information.
Identifying a Dermatologist or Skincare Specialist
Selecting a dermatologist or skincare specialist involves careful consideration. Look for board certification and experience in treating acne. Check online reviews and recommendations from trusted sources. Inquire about their approach to acne treatment and their experience with salicylic acid. Understanding their treatment philosophy and their commitment to patient care will aid in making an informed decision.
Addressing Concerns and Questions
Open communication with your healthcare professional is paramount. Feel free to ask questions about salicylic acid’s application, potential side effects, and interactions with other products. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or doubts you may have. Your dermatologist or skincare specialist is there to guide you through the process and address any questions promptly. Transparent communication fosters a strong doctor-patient relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A thorough understanding of salicylic acid can help you make informed decisions about its use. This section addresses common questions to facilitate a clearer comprehension.
- What is the ideal concentration of salicylic acid for acne treatment? The optimal concentration varies depending on individual skin sensitivity. A dermatologist can recommend the appropriate concentration based on your skin’s condition and response. Starting with a lower concentration and gradually increasing it is often a prudent approach.
- How often should I apply salicylic acid? The frequency of application is determined by the product’s formulation and your skin’s response. A dermatologist will advise on the optimal application schedule. Over-application can lead to irritation and hinder the treatment’s effectiveness.
- Can salicylic acid be used with other acne treatments? Salicylic acid can be combined with other acne treatments, but a healthcare professional should assess potential interactions. Combining treatments without professional guidance could lead to unexpected reactions or complications.
- What are the potential long-term effects of salicylic acid use? Salicylic acid, when used appropriately, does not typically cause long-term adverse effects. However, long-term use should be monitored by a healthcare professional. Any unusual changes or persistent concerns should be brought to their attention.
- Is salicylic acid suitable for all skin types? Salicylic acid is generally well-tolerated, but some skin types may react differently. A dermatologist can assess your skin type and determine the suitability of salicylic acid.
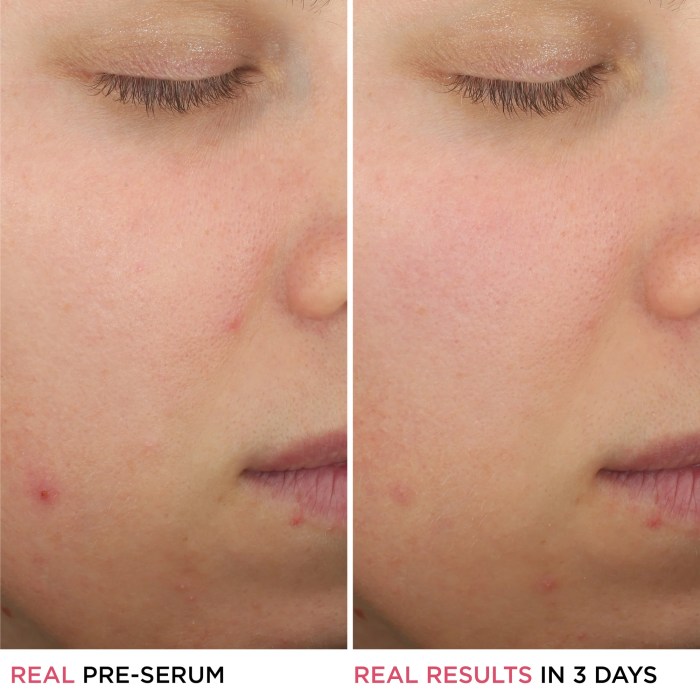
Visual Representation of Salicylic Acid’s Effects
Salicylic acid, a common ingredient in acne treatments, works by exfoliating the skin and unclogging pores. This process can lead to noticeable improvements in skin texture and appearance. Understanding the expected timeline and visual changes is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring successful treatment.Visual changes are typically subtle at first, but with consistent use, salicylic acid can effectively address various acne-related concerns.
The effectiveness and timeframe for results depend on factors like the severity of acne, individual skin type, and consistency of application.
Visible Changes in Skin Texture and Appearance
Salicylic acid’s exfoliating properties lead to a gradual improvement in skin texture. Initially, you might notice a slight reduction in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. As treatment continues, the skin becomes smoother and more even-toned. Blackheads and whiteheads may visibly decrease, and the overall appearance of acne lesions can lessen. Improvements are often most pronounced in areas with mild to moderate acne.
For severe acne, results may take longer to manifest.
Expected Timeframe for Seeing Results
The timeframe for seeing results from salicylic acid varies significantly. For mild acne, visible improvement might be seen within a few weeks of consistent application. Moderate acne may require several weeks to a few months of regular use to achieve significant results. Severe acne often needs longer treatment periods. It’s crucial to remember that results are gradual and not immediate.
Patience and consistent application are key. Consider consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice if results aren’t noticeable after a reasonable period.
Illustrative Progression of Acne Treatment
Imagine a series of photographs depicting a patient’s journey with salicylic acid.
- Initial Stage (Week 0-2): The initial image shows a skin condition characterized by active acne lesions, including inflamed papules, pustules, and possibly some comedones (blackheads/whiteheads). The skin texture appears uneven, with visible imperfections. This is the starting point for the treatment journey.
- Moderate Improvement (Week 2-4): The image shows a gradual reduction in the number and size of acne lesions. Inflammation appears to have subsided, and the skin looks slightly smoother. Some residual acne marks might still be present. The skin is less red, and blackheads and whiteheads are noticeably smaller or reduced in number.
- Significant Improvement (Week 4-8): The image reveals a noticeable decrease in acne lesions, with inflammation virtually gone. The skin texture is smoother and more even-toned. Residual acne marks are lighter and less prominent. The patient’s skin is noticeably clearer and more refined.
- Sustained Improvement (Week 8+): The image shows a clear and healthy complexion with minimal to no visible acne lesions. The skin texture is smooth, even-toned, and appears healthy. Any residual acne marks are barely noticeable, indicating a significant improvement in skin condition and texture.
Salicylic Acid Effects on Different Skin Types
Salicylic acid’s efficacy can vary based on skin type. Generally, salicylic acid is effective for most skin types, including oily, combination, and even normal skin. For sensitive skin, a lower concentration of salicylic acid may be necessary to minimize irritation. Results can differ based on skin tone and sensitivity. It’s important to start with a lower concentration and gradually increase if tolerated.
Always consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, salicylic acid presents a viable option for acne treatment, but its effectiveness and suitability vary based on individual skin types, acne severity, and other factors. This guide has highlighted the key considerations, from understanding the science behind its action to navigating potential side effects. Remember to consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and tailored treatment plans.
Common Queries
What are the common side effects of using salicylic acid?
Common side effects include skin redness, dryness, and irritation. The severity of these effects can vary depending on the concentration of salicylic acid and individual skin sensitivity. Patch testing is recommended before widespread use.
How often should I apply salicylic acid?
The optimal frequency depends on your skin’s sensitivity and the severity of your acne. Start with a lower frequency, such as once or twice a day, and gradually increase if your skin tolerates it well. Always avoid over-application.
Can salicylic acid be used on all types of acne?
While salicylic acid is effective for many types of acne, particularly comedonal acne, its suitability for inflammatory acne may vary. Consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific acne type.
How does salicylic acid work to treat acne?
Salicylic acid’s keratolytic properties help exfoliate dead skin cells, unclog pores, and reduce inflammation. It also works by targeting excess sebum production, which contributes to acne formation.