How to get rid of melasma? This guide delves into the complexities of this skin condition, offering a comprehensive approach to understanding, treating, and preventing melasma. From exploring its diverse causes and presentations to examining a range of effective treatments, including both topical and medical procedures, this resource will equip you with the knowledge to manage melasma effectively.
Melasma, a common skin discoloration, often appears as brownish or grayish patches. Understanding its origins and triggers is crucial to effective management. Hormonal fluctuations and sun exposure are key factors, and we’ll explore these in detail. This guide provides a structured approach to treatment, covering various methods, from topical creams and serums to more advanced medical interventions.
Understanding Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by the appearance of brownish or grayish-tan patches, typically on sun-exposed areas of the face. It’s often a cosmetic concern, but generally harmless. Understanding its causes, triggers, and presentation across different skin tones is crucial for effective management and treatment.Melasma, often referred to as chloasma, is a hyperpigmentation disorder. This means there’s an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
It’s important to distinguish melasma from other hyperpigmentation conditions like post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) or freckles, which may share similar visual characteristics but differ in their underlying causes and triggers. Melasma’s development is influenced by a complex interplay of factors.
Causes of Melasma
Melasma is predominantly associated with hormonal fluctuations and sun exposure. Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of melasma are more susceptible to developing the condition. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, or other hormonal imbalances can trigger or exacerbate melasma. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or tanning beds, is a major contributing factor.
Types of Melasma
Melasma typically presents in three main patterns:
- Centrofacial: This is the most common type, appearing as symmetrical patches on the central face, including the forehead, nose, cheeks, and upper lip. This pattern is often associated with hormonal influences.
- Peri-oral: This type involves patches concentrated around the mouth.
- Mandibular: This type manifests as patches along the jawline.
Presentation Across Skin Tones
Melasma’s appearance can vary depending on the individual’s skin tone. On lighter skin tones, melasma often appears as distinct, brownish-gray patches. On darker skin tones, melasma may manifest as a more diffuse darkening or a blotchy discoloration. The color intensity can also vary, from subtle darkening to more pronounced hyperpigmentation.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal changes are strongly linked to melasma development. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels, as experienced during pregnancy or while using hormonal contraceptives, are common triggers. These hormonal shifts can stimulate melanin production, leading to the characteristic brownish or grayish discoloration.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors play a crucial role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to melasma. Individuals with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition. This suggests a genetic component influencing melanin production and response to environmental factors. The inheritance pattern of melasma susceptibility is complex, not a simple dominant or recessive trait.
Treatment Approaches
Melasma, a common skin condition characterized by brown or gray patches, can be effectively managed through various treatment approaches. These strategies often involve a combination of lifestyle modifications and topical or professional treatments. Understanding the nuances of each approach is crucial for selecting the most suitable course of action for individual needs.Addressing melasma requires a multifaceted approach, tailoring the treatment plan to the patient’s specific circumstances and the severity of the condition.
Factors like skin type, sun exposure, and underlying medical conditions can influence the efficacy and safety of different treatments.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments remain a cornerstone of melasma management, providing a direct approach to addressing the pigmentation concerns. These treatments often target the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Various formulations, including creams, serums, and lotions, are available, each with its own unique ingredients and mechanisms of action.
Several topical treatments utilize ingredients that inhibit melanin production, reduce inflammation, or promote skin cell turnover. Commonly used ingredients include hydroquinone, azelaic acid, kojic acid, vitamin C, retinoids, and licorice extract. The choice of ingredients depends on the specific needs and preferences of the patient, as well as the severity and characteristics of their melasma.
Specific Topical Formulations
A range of topical formulations is available, each with unique combinations of ingredients designed to target various aspects of melasma. These formulations vary in their strength, concentration, and the specific combination of ingredients. Examples include:
- Hydroquinone Creams/Serums: Often used in higher concentrations, these formulations are known for their efficacy in reducing melanin production. However, long-term use can potentially lead to skin irritation and hyperpigmentation if not used appropriately.
- Azelaic Acid Creams/Serums: This ingredient is effective in reducing inflammation and inhibiting melanin production. It generally has a lower risk of side effects compared to hydroquinone. Formulations typically use a percentage of azelaic acid, ranging from low to medium concentration, depending on the specific product.
- Vitamin C Serums: These serums are potent antioxidants that can help brighten the skin and reduce inflammation. Vitamin C’s efficacy in melasma treatment is often combined with other treatments for improved outcomes.
- Retinoid Creams: Retinoids promote skin cell turnover, which can help to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. However, retinoids can sometimes cause dryness, peeling, or redness, especially when used in high concentrations. Careful application and monitoring are crucial.
Comparison of Topical Treatments
The following table provides a comparative overview of common topical treatments for melasma, highlighting their efficacy and potential side effects:
| Treatment | Ingredients | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroquinone 2% Cream | Hydroquinone | High (often effective but requires caution) | Potential skin irritation, hyperpigmentation (if used incorrectly or for extended periods), allergic reactions |
| Azelaic Acid 10% Gel | Azelaic Acid | Moderate to High (often well-tolerated) | Dryness, mild skin irritation |
| Kojic Acid 2% Cream | Kojic Acid | Moderate (can be effective for some individuals) | Mild skin irritation, potential allergic reactions |
| Vitamin C Serum (20% L-Ascorbic Acid) | L-Ascorbic Acid | Moderate (often used in combination with other treatments) | Skin irritation, redness |
| Retinoid Cream (0.025% Tretinoin) | Tretinoin | Moderate (effective in reducing hyperpigmentation, but can cause skin irritation) | Dryness, peeling, redness, increased sun sensitivity |
Lifestyle Modifications
Melasma, a skin condition characterized by brownish or grayish patches, can be influenced by various lifestyle factors. Understanding these factors and implementing appropriate modifications can contribute to improved management and potentially reduce the appearance of melasma. These modifications, alongside professional treatments, can be an integral part of a comprehensive approach to managing the condition.
Exacerbating Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can exacerbate melasma, particularly those involving sun exposure. Factors such as hormonal fluctuations, stress, and inadequate skin care routines can also contribute to its development or worsening. Consistent awareness and adjustments to these factors can be beneficial in managing melasma.
Sun Protection
Sun exposure is a critical factor in melasma management. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight is a major contributor to melasma development and worsening. Consistent and diligent sun protection is paramount. This involves employing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher, consistently throughout the day, even on cloudy days. Seeking shade during peak sun hours is also recommended.
Regular use of protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, further enhances sun protection. Remember, prolonged sun exposure, even on overcast days, can still trigger or worsen melasma.
Diet and Hydration
A healthy diet and adequate hydration are crucial for overall skin health and can positively impact melasma management. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports skin’s natural processes and can promote a healthier complexion. Hydration is equally important, as proper hydration helps maintain skin elasticity and supports cellular function. Maintaining a consistent hydration level contributes to the overall health and appearance of the skin.
Dietary Recommendations
Maintaining a healthy diet supports skin health. A diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help protect the skin from damage. Include fruits and vegetables in your diet, especially those rich in these antioxidants. Foods rich in vitamin C, like citrus fruits and berries, and foods rich in vitamin E, such as nuts and seeds, are beneficial.
Furthermore, consuming foods rich in collagen, such as fish and eggs, can contribute to skin firmness. Hydration is also essential; water intake should be sufficient to maintain skin hydration and overall well-being. A diet that supports overall health, with sufficient intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, is key.
- Fruits and vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and vitamins, supporting overall skin health.
- Citrus fruits: Excellent source of vitamin C, a potent antioxidant.
- Berries: Contain high levels of antioxidants, beneficial for skin health.
- Nuts and seeds: Good sources of vitamin E, an antioxidant important for skin health.
- Fish and eggs: Contain collagen-promoting nutrients, beneficial for skin firmness.
- Water: Essential for hydration, supporting skin health and elasticity.
Medical Procedures
Medical procedures offer various approaches to melasma treatment, ranging from superficial exfoliation to more targeted therapies. These methods can be effective when combined with lifestyle modifications and topical treatments. The selection of a procedure depends on the severity and extent of melasma, individual skin type, and the desired outcome.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels utilize chemical solutions to remove the top layers of skin, revealing healthier, brighter skin underneath. This process can help lighten hyperpigmentation and improve skin texture. Different concentrations of chemical solutions cater to various skin types and depths of treatment. Mild peels, such as those containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs), can be effective for mild melasma and are often used as a maintenance treatment.
Getting rid of melasma can be tricky, but focusing on a good skincare routine, especially one tailored for dark skin types like skincare for dark skin , is key. This often involves using products that address hyperpigmentation while protecting the skin from sun damage. Consistent application of sunscreen and a healthy lifestyle are also crucial components in the battle against melasma.
Medium peels, such as those using trichloroacetic acid (TCA), can address moderate melasma, but carry a higher risk of side effects. Deep peels, employing stronger acids, are reserved for severe cases and require careful consideration of potential complications. Preparation typically involves thorough skin cleansing and a consultation to assess skin health and suitability for the procedure. Recovery time varies depending on the peel’s depth, ranging from a few days to several weeks.
Possible side effects include redness, swelling, and temporary skin sensitivity.
Laser Treatments
Laser treatments utilize precisely targeted beams of light to address melasma. Different laser types target various skin layers and pigment types. Q-switched lasers, for example, can selectively break down melanin, which contributes to melasma. This process can lighten hyperpigmented areas and improve skin tone. The procedure involves applying the laser to the affected area in controlled pulses.
Preparation includes skin cleansing and assessment to determine the appropriate laser type and parameters. Recovery time is generally shorter than other procedures, with minimal downtime expected. Potential risks include temporary redness, mild swelling, and, in rare cases, scarring. Results can vary depending on the severity of melasma and the individual’s skin response.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion involves gently exfoliating the skin using tiny crystals or a device that physically removes the top layer of skin. This process can improve skin texture and tone, potentially lightening melasma. The procedure involves gently rubbing the skin with the exfoliating agent. Preparation includes thorough cleansing and assessment of skin sensitivity. Recovery time is usually short, with minimal discomfort anticipated.
Potential risks are limited, typically involving mild redness and skin sensitivity. Microdermabrasion is often used as a complementary treatment to other therapies for melasma, contributing to a gradual improvement in skin tone.
Summary of Medical Procedures for Melasma Treatment, How to get rid of melasma
| Procedure | Description | Recovery Time | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Peels | Use of chemical solutions to exfoliate skin layers, targeting hyperpigmentation. | Days to weeks, depending on peel depth. | Redness, swelling, temporary skin sensitivity. |
| Laser Treatments | Precise application of laser light to target and break down melanin, lightening hyperpigmented areas. | Minimal downtime. | Temporary redness, mild swelling, rare scarring. |
| Microdermabrasion | Gentle exfoliation of skin using crystals or a device to improve texture and tone. | Short recovery period. | Mild redness, skin sensitivity. |
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Many individuals explore home remedies and natural treatments for melasma alongside conventional therapies. While these approaches may offer potential benefits, it’s crucial to understand that their effectiveness is often not supported by rigorous scientific evidence and may not be sufficient on their own to completely resolve melasma. Consult with a dermatologist before relying solely on home remedies, especially if the melasma is severe or persistent.Home remedies and natural treatments for melasma frequently involve topical applications.
These remedies often claim to lighten the skin or reduce inflammation, potentially alleviating the appearance of melasma. However, the efficacy of these treatments can vary significantly, and results are not guaranteed. It’s important to proceed with caution and be aware that some ingredients might cause adverse reactions in certain individuals.
Common Home Remedies
A variety of home remedies are touted for their potential to address melasma. These approaches often involve topical application of ingredients found in nature, and may be combined with lifestyle modifications. The effectiveness of these remedies is often anecdotal and not supported by robust clinical studies.
- Lemon Juice: Lemon juice is frequently recommended for its purported lightening properties. It contains citric acid, which may theoretically lighten the skin. However, lemon juice can also cause skin irritation and sun sensitivity. Direct application may lead to skin discoloration in some individuals.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel is another popular home remedy, often claimed to soothe inflammation and promote skin healing. It may provide some relief from irritation, but its effectiveness in reducing melasma is not scientifically proven.
- Turmeric: Turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, is sometimes used topically for melasma. Its active component, curcumin, may have some lightening effects, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in treating melasma.
- Yogurt and Honey: Yogurt and honey, due to their moisturizing and potentially anti-inflammatory properties, are sometimes used in homemade masks. However, there’s no strong scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness in treating melasma.
Natural Ingredients for Topical Use
Several natural ingredients are frequently used in home remedies for melasma. Understanding their purported effects is important for informed decision-making.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that may help protect the skin from damage. Some believe it can reduce pigmentation, but more research is necessary to definitively prove its effectiveness for melasma.
- Kojic Acid: Kojic acid, derived from certain fungi, is sometimes used in skin lightening products. It’s thought to inhibit the production of melanin, but further research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety for treating melasma.
- Licorice Root Extract: Licorice root extract is another ingredient used in some topical treatments. It is believed to reduce melanin production, but more robust studies are needed to determine its efficacy for melasma.
Scientific Evidence
The scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of natural remedies for melasma is often limited. While some ingredients may have purported benefits, further clinical trials are necessary to confirm their effectiveness and safety. Results may vary greatly depending on individual factors.
List of Ingredients in Natural Remedies
- Lemon juice
- Aloe vera gel
- Turmeric
- Yogurt
- Honey
- Vitamin C
- Kojic acid
- Licorice root extract
Prevention Strategies
Melasma, while often treatable, can unfortunately recur if preventative measures aren’t consistently implemented. A proactive approach, encompassing sun protection and lifestyle adjustments, is crucial for long-term management and minimizing the risk of recurrence. These strategies are vital for individuals with a predisposition to melasma or those who have experienced it in the past.Effective prevention hinges on understanding the key triggers and consistently employing protective measures.
By integrating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of melasma returning.
Sun Protection Strategies
Consistent sun protection is paramount in preventing melasma recurrence. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, both UVA and UVB, is a primary driver of melasma development. Therefore, shielding the skin from the sun’s harmful rays is essential.
- Daily Application of Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Employing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is a fundamental step. This means the sunscreen should protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Reapplication every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating, is critical for maintaining adequate protection. For example, individuals engaging in outdoor activities like hiking or gardening should reapply sunscreen more often.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves and wide-brimmed hats, provides an additional layer of defense. This is particularly beneficial during peak sun hours and for outdoor activities. For example, a light, breathable long-sleeved shirt can provide considerable protection from the sun’s rays, while a wide-brimmed hat shields the face and neck.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, seek shade during the most intense sun hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. This can significantly reduce direct sun exposure. For example, taking breaks in shaded areas during outdoor activities can greatly minimize sun exposure.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle adjustments can complement sun protection measures in preventing melasma recurrence. These adjustments can contribute to overall skin health and reduce potential triggers.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can potentially exacerbate various skin conditions, including melasma. Adopting stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can be beneficial. For example, practicing mindfulness techniques can help regulate stress levels, which in turn can potentially positively impact skin health.
- Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration by drinking sufficient water daily can contribute to overall skin health. For example, consuming at least eight glasses of water daily can help maintain skin hydration and elasticity, reducing potential skin sensitivities.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants may support healthy skin and potentially mitigate factors contributing to melasma. For example, a diet rich in antioxidants can potentially help protect the skin from oxidative stress, a factor that might be involved in melasma development.
Preventive Measures for Specific Situations
Strategies for sun protection and lifestyle adjustments should be adapted to different situations, such as outdoor activities and travel.
| Situation | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
| Outdoor Activities | Increase sunscreen application frequency, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours. |
| Travel | Pack appropriate sun protection gear, be mindful of local sun exposure patterns, and adjust routines according to destination. |
Skincare Routine for Melasma Management
A consistent and tailored skincare routine is crucial for managing melasma. By incorporating products and practices that address the specific needs of your skin, you can effectively control melasma’s progression and minimize its appearance. This routine should be viewed as a long-term commitment, as visible improvements often take time and consistent effort.
Comprehensive Skincare Routine for Melasma
A comprehensive skincare routine for melasma management should focus on protecting the skin from further irritation, promoting even skin tone, and supporting the skin’s natural healing processes. This routine should be adjusted to individual skin types and sensitivities.
| Step | Action | Product Examples | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gentle Cleansing | Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser to remove dirt, makeup, and excess oil without stripping the skin’s natural moisture barrier. | Cleansers with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, aloe vera, or ceramides. Avoid harsh soaps and sulfates. | Twice daily, morning and evening. |
| 2. Targeted Serum Application | Apply a serum specifically formulated to address melasma. These serums often contain ingredients like vitamin C, azelaic acid, or kojic acid to help even out skin tone and reduce hyperpigmentation. | Serums with vitamin C, azelaic acid, or kojic acid. | Once daily, ideally in the morning. |
| 3. Sunscreen Application | Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect the skin from harmful UV rays, a major contributor to melasma development. | Sunscreens with mineral filters like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. | Daily, every time you are exposed to sunlight. Reapply every two hours. |
| 4. Exfoliation (Optional) | Gentle exfoliation can help remove dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover and potentially improving the appearance of melasma. | Chemical exfoliants containing glycolic acid, lactic acid, or salicylic acid. | 1-2 times per week, depending on your skin’s tolerance. |
| 5. Moisturizing | Moisturize the skin to maintain its hydration and support its natural barrier function. | Moisturizers containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or glycerin. | Twice daily, morning and evening. |
| 6. Nighttime Treatment (Optional) | Consider incorporating a targeted nighttime treatment, such as retinoids (with caution), to promote skin cell turnover and potentially reduce hyperpigmentation. | Retinoids, with caution and under medical supervision. | Once daily, at night. |
Product Selection Considerations
Selecting the right products is vital for melasma management. Consider ingredients like vitamin C, azelaic acid, and kojic acid, known for their potential to lighten hyperpigmentation. Always choose fragrance-free products to minimize irritation. Prioritize broad-spectrum sunscreens with a high SPF to shield skin from harmful UV radiation.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can complement your skincare routine. Sufficient sleep, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and stress management can positively impact overall skin health and potentially contribute to reducing melasma. Hydration is also key to maintaining skin health.
Understanding Skin Sensitivity
Skin sensitivity is a crucial factor to consider when addressing melasma. Many individuals experience varying degrees of skin sensitivity, which can significantly impact the efficacy and safety of melasma treatments. Recognizing these sensitivities is vital for tailoring a personalized approach and preventing potential adverse reactions.Skin sensitivity manifests in various ways, ranging from mild discomfort to more severe reactions.
It’s essential to understand that skin sensitivity can affect how the skin responds to various products and treatments, including those used to target melasma. A crucial aspect of effective melasma management is understanding how individual skin reacts to different treatments.
Impact of Skin Sensitivity on Melasma Treatment
Skin sensitivity can influence the effectiveness and safety of melasma treatments. A sensitive skin type may exhibit heightened reactions to ingredients in topical treatments, leading to irritation, redness, or inflammation. These reactions can hinder treatment progress and potentially exacerbate melasma, particularly if the treatment isn’t properly adjusted to the individual’s skin type. Conversely, a less sensitive skin type might respond well to a broader range of treatments.
Identifying Individual Skin Sensitivities
Identifying individual skin sensitivities is paramount in developing a safe and effective melasma treatment plan. This process often involves a gradual introduction of new products or treatments to assess how the skin reacts. Observing the skin’s response over time is crucial for identifying potential sensitivities. A thorough consultation with a dermatologist or skincare professional can help pinpoint specific triggers and develop personalized strategies.
Fading melasma often involves a targeted approach, and a key element is a simple skincare routine. Adopting a minimalist skincare routine can significantly help. This usually means focusing on products specifically formulated to address hyperpigmentation, while avoiding unnecessary ingredients that could irritate the skin and potentially worsen the condition. Ultimately, consistency with a well-chosen routine is crucial for managing melasma effectively.
Common Skin Sensitivities and Their Impact on Melasma
Various factors can contribute to skin sensitivity. Some common sensitivities include:
- Irritants: Certain ingredients, such as fragrances, preservatives, or harsh exfoliants, can trigger irritation and inflammation. This can be especially problematic when addressing melasma, as the sensitive skin may react negatively to active ingredients designed to target pigmentation.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to specific ingredients can manifest as hives, itching, or swelling. Identifying and avoiding these allergens is essential for preventing reactions and optimizing melasma treatment.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to harsh weather conditions, pollution, or UV radiation can contribute to skin sensitivity. For instance, sun exposure can worsen existing melasma and increase skin sensitivity, making treatments less effective or even causing adverse reactions.
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema, rosacea, or psoriasis can make the skin more susceptible to irritation and sensitivity. Understanding these underlying conditions is critical when developing a melasma treatment plan.
Gradual Introduction of New Treatments
A gradual introduction of new treatments is crucial for managing skin sensitivity during melasma treatment. Starting with a small amount of a new product or treatment and observing the skin’s reaction over a period of time (e.g., a few days) is essential. If no adverse reaction occurs, the product can be gradually increased. This approach minimizes the risk of severe reactions and allows for better management of potential sensitivities.
Professional Consultation
Seeking professional guidance from a dermatologist or skincare specialist is crucial in managing melasma effectively. A personalized approach, tailored to individual skin type, concerns, and medical history, is essential for achieving optimal results. A professional evaluation can pinpoint the underlying causes of melasma, ensuring the most appropriate and safe treatment strategy.A dermatologist possesses specialized knowledge and expertise in diagnosing and treating skin conditions, including melasma.
Their experience allows them to accurately assess the severity and type of melasma, enabling the development of a customized treatment plan. This individualized approach significantly improves the chances of successful melasma management and minimizes potential side effects.
Importance of a Personalized Treatment Plan
A personalized treatment plan is paramount in managing melasma effectively. A dermatologist will consider various factors, including the individual’s skin type, medical history, and lifestyle. This holistic approach ensures that the treatment strategy is both effective and safe. This approach is crucial for long-term success, avoiding potential skin irritations or complications that may arise from generic treatments.
Dermatologist’s Role in Evaluating and Treating Melasma
A dermatologist plays a vital role in evaluating and treating melasma. Their expertise extends beyond identifying the type and severity of melasma; they also consider potential underlying causes, such as hormonal fluctuations or certain medications. This comprehensive evaluation allows for the development of a tailored treatment plan. The dermatologist’s role includes monitoring the effectiveness of the treatment, adjusting the plan as needed, and educating the patient about proper skincare practices.
Examples of Questions to Ask a Dermatologist about Melasma
Effective communication with a dermatologist is essential for a successful melasma treatment journey. Here are examples of questions you can ask:
- What is the likely cause of my melasma, based on my medical history and skin characteristics?
- What are the potential risks and benefits of different treatment options, including topical creams, lasers, or other procedures, and how do they fit my lifestyle?
- What is the expected duration of treatment, and what are the realistic outcomes I should anticipate?
- What is a suitable skincare routine to maintain and improve my skin’s health during and after treatment?
- Are there any potential side effects associated with the recommended treatments, and how can they be managed?
- How frequently should I follow up for monitoring and adjustments to my treatment plan?
Long-Term Management: How To Get Rid Of Melasma
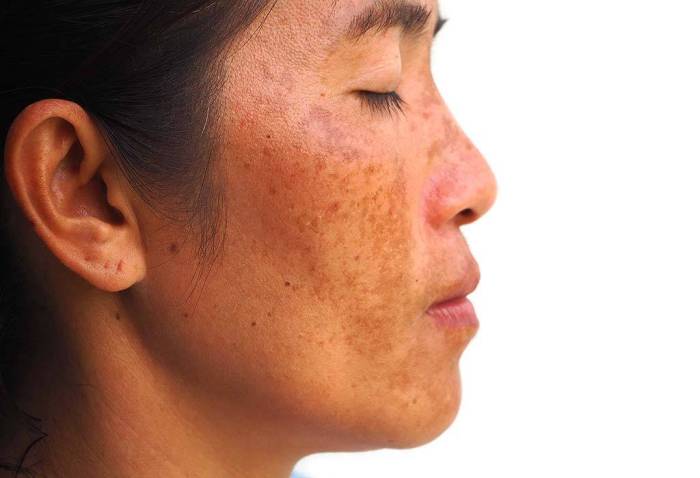
Melasma, while treatable, often requires a long-term approach. Effective management extends beyond the initial treatment phase and involves sustained lifestyle modifications and consistent monitoring of skin responses. This commitment ensures the best possible outcomes and minimizes the risk of recurrence.Melasma’s persistence underscores the need for proactive, long-term strategies. This proactive approach addresses the root causes of melasma and empowers individuals to maintain healthy skin.
It’s crucial to understand that complete elimination of melasma is not always achievable, and ongoing effort is necessary to manage its appearance and prevent worsening.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Management
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a significant role in managing melasma long-term. These modifications extend beyond the initial treatment period and are crucial for preventing recurrence and maintaining healthy skin.
- Sunscreen Application: Daily, broad-spectrum sunscreen application with an SPF of 30 or higher is essential. Regular application, even on cloudy days, significantly reduces sun exposure, a key trigger for melasma development. Re-application every two hours, or more frequently if sweating or swimming, is critical for maintaining protection.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins can support overall skin health and potentially mitigate the effects of melasma. Fruits, vegetables, and foods with high vitamin C and E content are beneficial. Hydration is crucial for overall health, including skin hydration.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate skin conditions. Practices like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can help manage stress and support skin health.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing sleep allows the body to repair and rejuvenate, promoting healthy skin cell turnover. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
Regular monitoring of the skin’s response to treatment is vital. This involves observing any changes in melasma’s appearance and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. Professional consultation is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of treatments and making adjustments.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a dermatologist to assess melasma’s progression and discuss adjustments to the treatment plan. These visits provide opportunities to monitor skin health and evaluate the effectiveness of the current approach.
- Skin Evaluation: Closely monitor the skin’s response to treatments. Note any changes in the appearance of melasma, such as fading, darkening, or the appearance of new patches. Document these observations and discuss them with your dermatologist.
- Treatment Adjustments: Adjustments to the treatment plan might include increasing the frequency of topical treatments, incorporating additional therapies, or adjusting the type of treatment if necessary. Adjustments should always be guided by a medical professional.
Patience and Consistency in Melasma Management
Melasma management is a process that requires patience and consistency. Significant improvement may not be immediate, and maintaining a consistent approach is crucial for long-term success. Expecting rapid results can be frustrating, and understanding the gradual nature of improvement is vital.
- Gradual Improvement: Melasma often improves gradually over time. Be prepared for a period of ongoing treatment and be patient with the process. Consistency in adhering to treatment plans and lifestyle modifications is key to achieving the best long-term results.
- Long-Term Commitment: Remember that melasma management is a long-term commitment. Consistency in adhering to the prescribed treatment plan, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring is essential for sustainable results.
- Professional Guidance: Seek guidance from a dermatologist throughout the process. They can offer personalized advice and adjust the treatment plan based on individual needs and responses.
Addressing Concerns and Myths
Melasma, a common skin condition, can evoke a range of emotions and concerns. Misinformation and myths surrounding its treatment and prevention can further complicate matters. Understanding the facts is crucial for effective management and achieving positive outcomes.Many individuals grapple with misconceptions about melasma, leading to frustration and potentially ineffective treatment approaches. Separating fact from fiction is key to navigating this condition successfully.
Common Misconceptions about Melasma
Common misconceptions often stem from a lack of comprehensive information. Many believe melasma is solely caused by sun exposure, overlooking other contributing factors. Some also harbor concerns about the long-term effects of treatment, or they may be uncertain about the potential for complete resolution.
- Melasma is primarily caused by sun exposure, but other factors like hormonal fluctuations and genetics play a significant role. A combination of these influences often contributes to the development of melasma.
- Complete resolution of melasma is achievable for many individuals through a comprehensive approach that addresses all contributing factors.
- Melasma treatments may have temporary side effects, but most are manageable and temporary. Consultations with dermatologists can provide guidance on potential side effects.
- Melasma is not contagious and does not indicate underlying health issues. It is a common skin condition that can be managed effectively.
Correcting Common Myths about Melasma Treatment
Some widely circulated myths surrounding melasma treatment can hinder progress. Addressing these misconceptions is vital for making informed decisions.
- Many home remedies, while sometimes offering temporary improvements, do not consistently address the underlying causes of melasma. Professional dermatological treatments often offer more sustained results.
- While some ingredients may show promise in some cases, there is limited rigorous scientific evidence to support their effectiveness in treating melasma. A multifaceted approach that includes professional advice and consistent skincare is often recommended.
- Melasma treatment does not always require invasive procedures. Many effective treatments are available, including topical medications and professional consultations.
- The effectiveness of any treatment varies from individual to individual, and it may take several weeks or months to see noticeable results. Consistency and patience are crucial for achieving lasting results.
Importance of Evidence-Based Information
Evidence-based information provides a solid foundation for managing melasma. Reliable sources, such as dermatological journals and reputable medical organizations, offer crucial insights into treatment options and best practices.
- Reliable sources provide accurate information on melasma, empowering individuals to make informed decisions regarding treatment and management.
- Staying updated on the latest research and advancements in melasma treatment can ensure individuals are utilizing the most effective and up-to-date strategies.
- Evidence-based information offers a reliable guide for individuals seeking a deeper understanding of melasma and its effective management.
Reassurance and Support for Individuals with Melasma
Melasma can be a challenging condition to navigate, but with the right approach, it can be managed successfully.
- Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and online communities. Sharing experiences and finding solidarity can help in managing the emotional aspects of living with melasma.
- Positive self-care practices, such as stress reduction techniques and healthy lifestyle choices, can contribute to overall well-being and improve skin health.
- Understanding the multifaceted nature of melasma, including its potential causes, is essential for effectively addressing the condition.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, managing melasma involves a multi-faceted strategy encompassing understanding its causes, implementing appropriate treatments, and adopting preventative measures. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, encompassing lifestyle modifications, medical procedures, and home remedies. Remember that consistency, patience, and professional guidance are key to achieving lasting results. Consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and tailored treatment plans.
Essential FAQs
What are the common triggers for melasma?
Hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control pills), sun exposure, and genetics are common triggers. Certain medications can also contribute.
Are there home remedies for melasma?
Some home remedies, like using certain plant extracts topically, are purported to help, but their effectiveness varies and scientific evidence is often limited. Always consult a dermatologist before relying solely on home remedies.
How long does melasma treatment typically take?
Treatment timelines vary significantly depending on the severity of melasma, the chosen treatment method, and individual skin response. Consistency and patience are vital.
Can melasma be completely cured?
While melasma can often be significantly improved, complete eradication is not always possible for all individuals. Ongoing management and prevention are crucial.





